When using image files, you have certainly stumbled across different file extensions before. But what exactly is behind PNG, JPEG, EPS & Co? And which format is suitable for which application? Read all relevant information about the different image formats below.
No desire to read? Listen to the blogcast here:
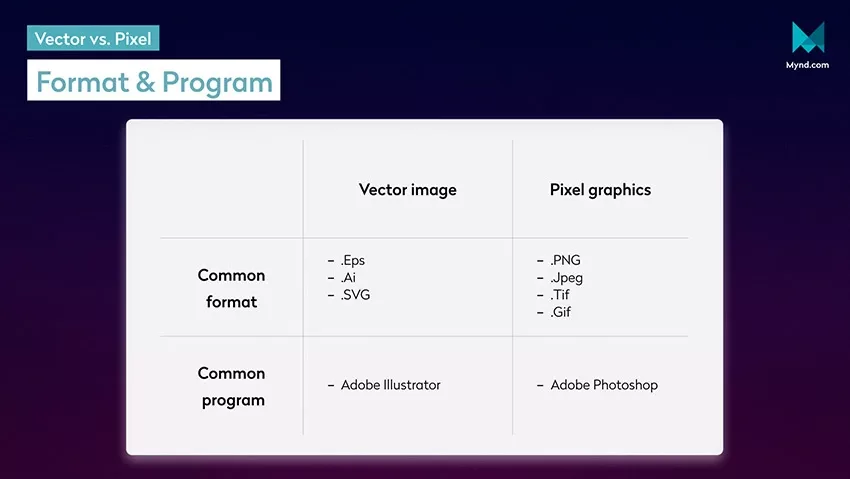
Graphics are divided into two basic formats:
- Vector graphics.
- Pixel graphics.
Vektorgraphics.
A vector graphic contains line and curve information. These are defined by vectors that describe the graph based on its geometric properties. Objects are not defined using small pixels, but according to the description of their elements. While a circle in a pixel graphic consists of many individual pixels, the circle in a vector graphic contains information such as the diameter of the circle, the color, and the position of the center.
The most important output formats of vector graphics.
- .Ai (Adobe Illustrator): .Ai is the vector-based file format of Adobe Illustrator. If the file does not contain pixel images, scaling is possible with small file sizes. This is a so-called proprietary file format. This means that the file format depends almost entirely on the software (in this case Adobe Illustrator), and further use outside this software is very difficult.
- .EPS (Encapsulated Postscript): PostScript, which can contain pixel images and vector graphics. The image quality is high despite the small file size. Additional changes of the file are only possible to a limited extent. Likewise, existing pixel images in the file cannot be scaled without loss of quality.
- .SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): .SVG is based on XML and displays two-dimensional vector graphics online. Since SVG files can be read by a large number of browsers and software, they have a higher usage rate on the web than .ai or .eps files, for example.
Advantages of vector graphics.
Vector graphics can be scaled with very little loss of quality, i.e. the size can be changed at will without impairing the image quality. The graphics have a small file size and good compression possibilities. Properties of curves, lines, and areas can be edited. A rasterization from vector to pixel graphics, i.e. a conversion of the file into a pixel format, is much easier than vice versa.

In contrast to pixel graphics (right image), vector graphics (left image) can be scaled without loss of quality.
Disadvantages of vector graphics.
In contrast to pixel graphics, processing is more complex. In order to reproduce a vector graphic, a rasterization is necessary. Likewise, vector graphics are supported by fewer programs than pixel graphics.
Areas of application.
Vector graphics are particularly suitable for geometric graphics and figures as well as for logos, fonts, and technical drawings.
Most popular program.
Adobe Illustrator is the most popular graphics and drawing program for editing vector-based files.
Vector and pixel graphics have different formats that can be edited in different programs.
Pixel graphics.
A pixel graphic consists of a large number of square pixels, each of which is assigned a color. The size of the graphic depends on the number of pixels. The image resolution is therefore determined by the number of pixels that determine the height and width of a graphic.
The most important output formats of pixel graphics.
- .JPEG: JPEG files contain up to 16.7 million colors. The file size is relatively small, whereby compression is accompanied by data loss. The files are primarily used when a small file size is more important than maximum image quality, for example to optimize loading times of websites.
- .PNG: PNG files have 16.7 million colors and the 8-bit alpha channel, which ensures the transparency of the individual pixels as well as the color information. The files allow lossless compression. PNG files are mainly suitable for processing graphics with transparency and transparency gradients as well as complex, high-quality images where the file size can be neglected.
- .GIF: GIF files have 256 colors and transparency. These are simple animations as image files which allow lossless compression. The application is exclusively intended for web graphics with few colors, as well as small GIF animations.
The GIF format is suitable for simple image animations.
- TIF: TIF graphics have various compression methods and a color depth of 32 bits. Color depth is the number of gradations within a gradient. You will find their application in high-quality image files with unaltered representation and high-color depth.
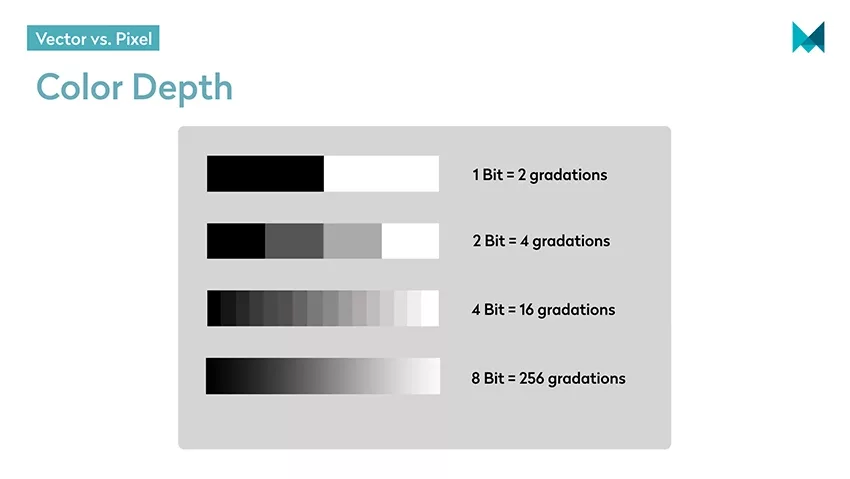
The number of gradations determines the color depth.
Advantages of pixel graphics.
Pixel graphics have a program-independent file format as well as various graphic formats for different areas of application. In addition, they contain a wealth of color gradations. Surfaces can be copied and moved. Each individual pixel can be edited separately.
Disadvantages of pixel graphics.
Pixel graphics cannot be scaled without loss of quality. The file size is correspondingly high due to the often-detailed graphics. While a transformation from a vector to a pixel graphic is largely possible without any problems, the reverse process, the vectorization of a pixel graphic, is a complex undertaking.
Areas of application.
First and foremost, pixel graphics are used for image processing and are suitable for creating complex, artistic graphics.
Most popular program.
Adobe Photoshop is the most popular image editing program for pixel graphics.
Ppi and dpi.
The specifications in ppi and dpi refer only to pixel-based raster graphics. A subsequent change of the sizes is not possible, therefore graphics must be created in the correct size in advance.
Pixel per Inch (ppi).
Ppi indicates the resolution, i.e. how many pixels are output per inch. Ppi is responsible for the image size and quality.
Dots per Inch (dpi).
Dpi indicates how many pressure points lie on one inch. This specification is not relevant for the image size, but only for the print quality.
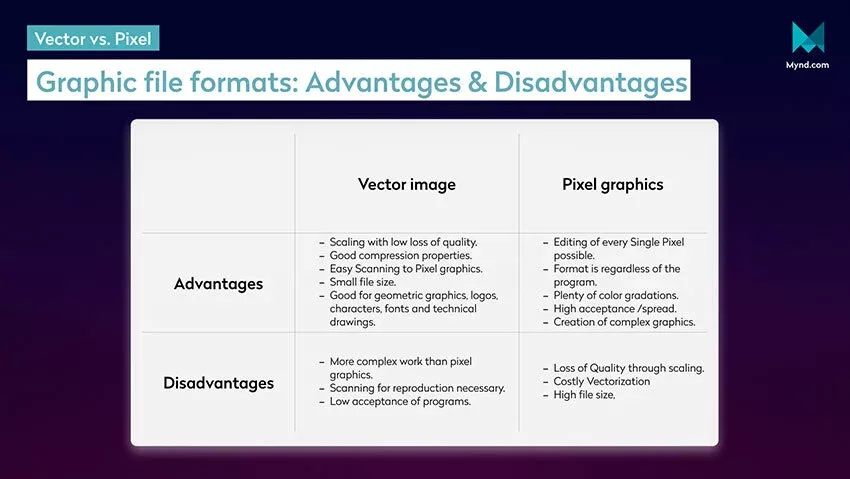
All advantages and disadvantages of vector and pixel graphics at a glance.
Correct use is crucial.
A large amount of information plays a decisive role in the correct and target-oriented use of graphics. Professional agencies have the necessary knowledge needed to handle graphics accordingly.



